
【Applied Energy】液态二氧化碳储能系统技术可行性研究:集成部件设计和变工况性能分析
日期:2023-11-02 点击数:
Title:A technical feasibility study of a liquid carbon dioxide energy storage system: Integrated component design and off-design performance analysis
【Applied Energy】液态二氧化碳储能系统技术可行性研究:集成部件设计和变工况性能分析
原文链接:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0306261923011613

Highlights
(1) 研发了液态CO2储能系统的变工况性能预测模型
(2) 揭示了不同负荷水平下系统的储-释能特性
(3) 提出了两种应用于系统储-释能过程的运行策略
(4) 获得了两种运行策略的最佳应用负荷范围
Research gap
液态二氧化碳储能(LCES)系统在充分利用可再生能源方面具有巨大潜力。本研究全面探究了LCES系统的技术可行性,包括关键部件设计、变工况性能分析和运行策略制定。这些工作为LCES系统在不同工况下的稳定运行提供了重要的参考依据。
摘要
液态二氧化碳(CO2)储能(LCES)系统作为一种能够实现能量时移和平抑电力波动的技术方法,目前受到广泛的关注。本文旨在研究液态CO2储能系统在不同运行策略下的设计以及变工况性能,以揭示系统储释能过程的耦合匹配调节机制。首先,在初步设计叶轮机械部件和换热器的基础上,研发了用于预测系统设计性能和变工况性能的仿真模型,以评估系统的可行性。随后,分析了采用两种运行策略后系统的储释能性能,即定压储能-定压释能(CP-CP)运行策略和定压储能-滑压释能(CP-SP)运行策略。研究结果显示,在额定条件下,LCES系统的储能效率为61.83%,储能密度为21.92 kW·h·m−3。在定压储能运行策略下,随着输入负荷水平从80%增加到120%,系统的最大储能时间从5.15小时减少到3.36小时。当输出负荷水平从70%增加到120%时,在定压释能运行策略下,最大释能时间从5.48小时减少到3.31小时,而在滑压释能运行策略下则从5.60小时降低至3.30小时。此外,LCES系统的储能随着输入和输出负荷水平的升高呈现先增加后减少的趋势,而储能密度仅随输出负荷水平的增加而呈现抛物线变化趋势。综合分析来看,LCES系统在70%~100%负荷区间内释能时,宜采用CP-SP控制策略;而在100%~120%负荷区间内释能时,宜采用CP-CP控制策略。这些研究结论将为LCES在变工况条件下的稳定运行提供有价值的参考。
Abstract
Liquid carbon dioxide (CO2) energy storage (LCES) system is emerging as a promising solution for high energy storage density and smooth power fluctuations. This paper investigates the design and off-design performances of a LCES system under different operation strategies to reveal the coupling matching regulation mechanism of the charging and discharging processes. An off-design performance prediction model is developed based on preliminary designs of turbomachinery components and heat exchangers to evaluate the feasibility of the LCES system. The performances of the charging and discharging processes are analyzed under different load levels with two operation strategies: constant pressure charging and constant pressure discharging (CP-CP) operation strategy, and constant pressure charging and sliding pressure discharging (CP-SP) operation strategy. Results show that the LCES system has a round trip efficiency of 61.83% and an energy storage density of 21.92 kW·h·m−3 under the rated condition. As the input load level increases from 80% to 120%, the maximum charging time of the system decreases from 5.15 h to 3.36 h under the constant pressure operation strategy. When the output load level increases from 70% to 120%, the maximum discharging time of the system decreases from 5.48 h to 3.31 h under the constant pressure operation strategy and from 5.60 h to 3.30 h under the sliding pressure operation strategy. Besides, the round trip efficiency of the LCES system increases first and then decreases as both input and output load levels rise, while the energy storage density of the system follows a parabolic curve only with an increase in the output load levels. For better system performance, the CP-SP operation strategy and CP-CP operation strategy are more suitable for the system with output load levels of 70–100% and 100–120%, respectively. These achievements will provide a valuable reference for the stable operation of the LCES under off-design conditions.
Keywords(英文与中文)
Liquid carbon dioxide energy storage system 液态二氧化碳储能系统
Turbomachinery design 叶轮机械设计
Heat exchanger 换热器
Off-design analysis 变工况性能分析
Round trip efficiency 储能效率
Schematics
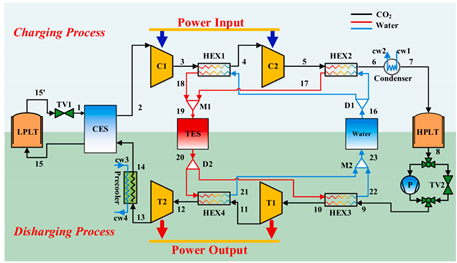
图1 LCES系统原理图
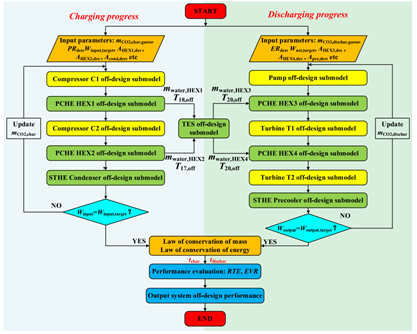
图2 LCES系统变工况性能仿真流程图
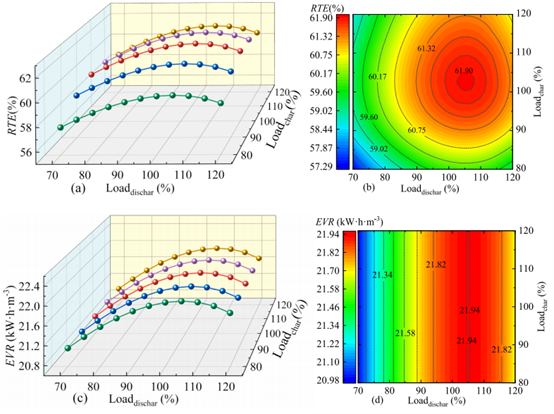
图3 LCES系统在CP-CP运行策略下的变工况性能
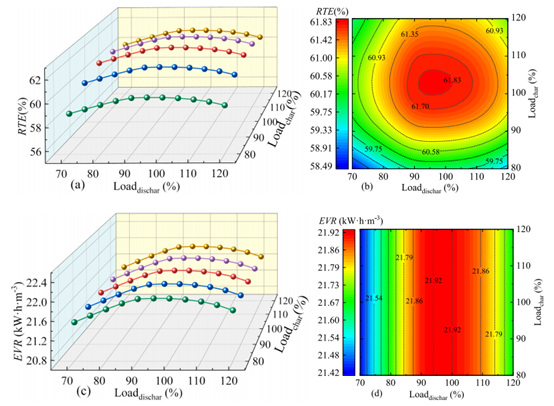
图4 LCES系统在CP-SP运行策略下的变工况性能
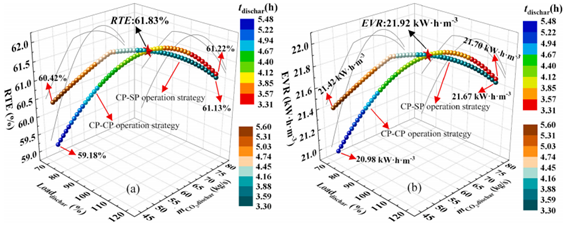
图5 不同运行策略下LCES系统性能对比
团队介绍(optional)
本研究由重庆大学能源与动力工程学院、郑州大学机械与动力工程学院以及西安交通大学能源与动力工程学院的研究人员共同完成。
通信作者简介:
吴闯,工学博士,硕士生导师。长期从事先进超临界二氧化碳循环、储能系统理论与技术、工质热稳定性与热分解机理、中低品位能源高效转换利用技术等研究。主持国家自然科学基金、中国博士后科学基金等项目多项。近年来,共发表高水平论文30余篇,其中以一作/通讯作者发表SCI论文16篇。
第一作者简介:
万玉珂,重庆大学硕士研究生,主要研究方向为液态二氧化碳储能系统优化设计及性能分析。


 设为首页
设为首页
 加入收藏
加入收藏
